ENVÍO GRATIS A LA UE, REINO UNIDO Y EE.UU.
The Benefits and Risks of Sunlight Exposure for Skin: The Essential Role of Sunscreen
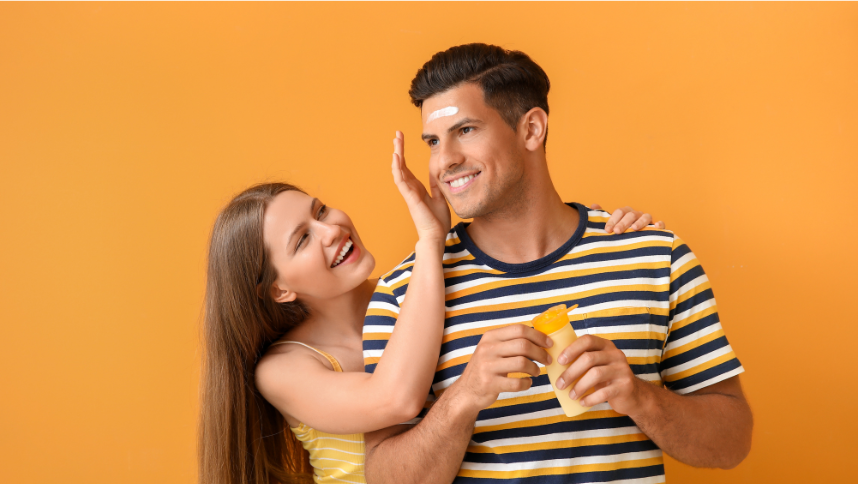

Sunlight is one of nature's greatest gifts, offering warmth, light, and essential vitamin D. However, like all good things, exposure to sunlight comes with its own set of benefits and risks, especially when it comes to our skin. The delicate balance of basking in the sun's rays while protecting our skin's health can be a challenge. Understanding this balance is crucial for maintaining healthy, youthful skin. Let's explore the benefits and risks of sunlight exposure for the skin and highlight the importance of sunscreen in your daily skincare routine.
The Dual Nature of Sunlight
Sunlight has been celebrated for centuries for its life-giving properties. It boosts our mood, regulates our sleep patterns, and synthesizes vitamin D, which is vital for bone health. However, prolonged and unprotected exposure to the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays can lead to a host of skin problems, including sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer.
To fully appreciate the dual nature of sunlight, we must delve deeper into its effects on the skin and the essential role of sunscreen in protecting against its harmful consequences.
The Benefits of Sunlight for Skin
Vitamin D Synthesis
One of the most well-known benefits of sunlight is its ability to stimulate the production of vitamin D in the skin. Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, promoting strong bones and overall health. A short period of sun exposure, about 10-15 minutes a few times a week, can significantly contribute to your body's vitamin D levels.
Mood Enhancement
Sunlight exposure triggers the release of serotonin, a hormone that boosts mood and promotes feelings of well-being and happiness. This is why we often feel more energized and positive after spending time outdoors on a sunny day.
Circadian Rhythm Regulation
Natural sunlight helps regulate our circadian rhythm, the body's internal clock that controls sleep-wake cycles. Regular exposure to sunlight during the day can improve sleep quality and help prevent sleep disorders.
Skin Conditions
Moderate sunlight exposure has been shown to improve certain skin conditions such as psoriasis, eczema, and acne. The UV rays in sunlight can help reduce inflammation and accelerate the healing process for these conditions.
The Risks of Sunlight for Skin
Sunburn
One of the most immediate and noticeable risks of excessive sunlight exposure is sunburn. Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to too much UV radiation, causing redness, pain, and peeling. Severe sunburns can lead to blisters and even systemic symptoms such as fever and nausea.
Premature Aging
Prolonged exposure to UV rays accelerates the aging process of the skin, leading to the development of wrinkles, fine lines, and age spots. This process, known as photoaging, results from the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers in the skin, which are essential for maintaining its elasticity and firmness.
Skin Cancer
The most serious risk associated with UV radiation is skin cancer. There are three main types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. UV radiation damages the DNA in skin cells, leading to mutations that can result in cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States.
Hyperpigmentation
Excessive sun exposure can also lead to hyperpigmentation, a condition where patches of skin become darker than the surrounding areas. This occurs due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Conditions such as melasma and age spots are examples of hyperpigmentation caused by UV exposure.
The Role of Sunscreen in Sun Protection
What is Sunscreen?
Sunscreen is a topical product designed to protect the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. It contains active ingredients that either absorb, reflect, or scatter UV rays, preventing them from penetrating the skin. Sunscreen is available in various forms, including lotions, creams, gels, and sprays, and is categorized by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF), which indicates the level of protection it provides against UVB rays.
Types of Sunscreen
There are two main types of sunscreen: chemical and physical (mineral).
-
Chemical Sunscreens: These contain organic compounds such as oxybenzone, avobenzone, and octinoxate that absorb UV radiation and convert it into heat, which is then released from the skin. Chemical sunscreens are often lightweight and easy to apply but can sometimes cause skin irritation.
-
Physical (Mineral) Sunscreens: These contain inorganic compounds like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide that sit on the skin's surface and reflect UV radiation away from the skin. Mineral sunscreens are generally well-tolerated, making them suitable for sensitive skin types.
How to Choose the Right Sunscreen
When selecting a sunscreen, it is important to consider the following factors:
-
Broad-Spectrum Protection: Choose a sunscreen that offers broad-spectrum protection, meaning it protects against both UVA and UVB rays. UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and contribute to premature aging, while UVB rays cause sunburn and play a significant role in the development of skin cancer.
-
SPF Rating: The SPF rating indicates the level of protection against UVB rays. For daily use, an SPF of 30 is recommended. For extended outdoor activities, a higher SPF may be necessary.
-
Skin Type: Consider your skin type when choosing a sunscreen. For example, if you have oily or acne-prone skin, look for a non-comedogenic formula that won't clog pores. If you have dry skin, opt for a hydrating sunscreen that provides additional moisture.
Proper Application of Sunscreen
To ensure optimal protection, it is crucial to apply sunscreen correctly:
- Timing: Apply 15-30 minutes before sun exposure to allow it to fully absorb into the skin.
- Amount: Use a generous amount of sunscreen to cover all exposed areas. A good rule of thumb is to use about a shot glass full for the entire body.
-
Reapplication: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
Embrace the Sun Safely with THAROS - Mineral Suscreen SPF30
At THAROS, we understand the importance of protecting your skin while embracing the sun's benefits. Our Mineral Suscreen SPF30 is specially formulated with natural, vegan, and sustainable ingredients to provide broad-spectrum protection against harmful UV rays. This lightweight, non-greasy sunscreen is perfect for daily use, ensuring your skin stays healthy, radiant, and youthful.
Don't let the fear of sun damage hold you back from enjoying the outdoors. By incorporating sunscreen into your daily routine, you can enjoy the sun's benefits while minimizing its risks. Remember, a little protection goes a long way in preserving your skin's health and beauty. So, step out, soak in the sun, and shine with confidence!